In the ever-evolving world of technology, understanding the various types of computer networks is crucial for both personal and professional growth. Computer networks are categorized based on their geographical coverage and functionality, which can significantly impact the way we communicate, share information, and access resources. Knowing the differences between Wide Area Networks (WAN), Local Area Networks (LAN), Personal Area Networks (PAN), and Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN) can help individuals and organizations make informed decisions about their networking needs.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of these four primary types of computer networks, detailing their characteristics, advantages, and typical applications. By the end of this exploration, you will have a clearer understanding of which network type suits your requirements best, whether you’re setting up a home network, managing a business infrastructure, or simply interested in the technology that connects us all.
Understanding Computer Networks
Computer networks are systems that interconnect computers and devices, allowing them to communicate and share resources. These networks can vary significantly in terms of size, complexity, and purpose. The primary classifications of computer networks are based on their geographical coverage, leading to the identification of WAN, LAN, PAN, and MAN. Let’s take a closer look at each type.
1. Local Area Network (LAN)
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and devices within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, or building. LANs are typically characterized by high data transfer rates and low latency, making them ideal for environments where multiple devices need to share resources like files, printers, and internet access.
Characteristics of LAN
- Limited Geographical Area: LANs usually cover a small area, often not exceeding a few kilometers.
- High Speed: Data transfer rates can reach up to 1 Gbps or higher.
- Low Cost: Setting up a LAN is generally inexpensive, using standard networking equipment like routers and switches.
- Easy Management: LANs are easier to manage and troubleshoot compared to larger networks.
Common Uses of LAN
LANs are widely used in various environments. Some common applications include:
- Home networking to connect multiple devices.
- Office environments for file sharing and collaboration.
- Educational institutions to facilitate learning through shared resources.
2. Wide Area Network (WAN)
A Wide Area Network (WAN) spans a large geographical area, often connecting multiple LANs across cities, countries, or even continents. WANs are essential for organizations that operate in multiple locations and require a reliable means of communication and data transfer.
Characteristics of WAN
- Extensive Coverage: WANs can cover vast distances, making them suitable for global connections.
- Slower Speeds: Data transfer rates are generally lower than LANs, often ranging from 56 Kbps to several hundred Mbps.
- Higher Cost: Setting up and maintaining a WAN can be expensive due to the need for leased telecommunication lines.
- Complex Management: WANs require more sophisticated management tools and protocols.
Common Uses of WAN
WANs are utilized in various scenarios, including:
- Connecting branch offices of a company.
- Providing internet access to remote locations.
- Facilitating communication between government agencies across regions.
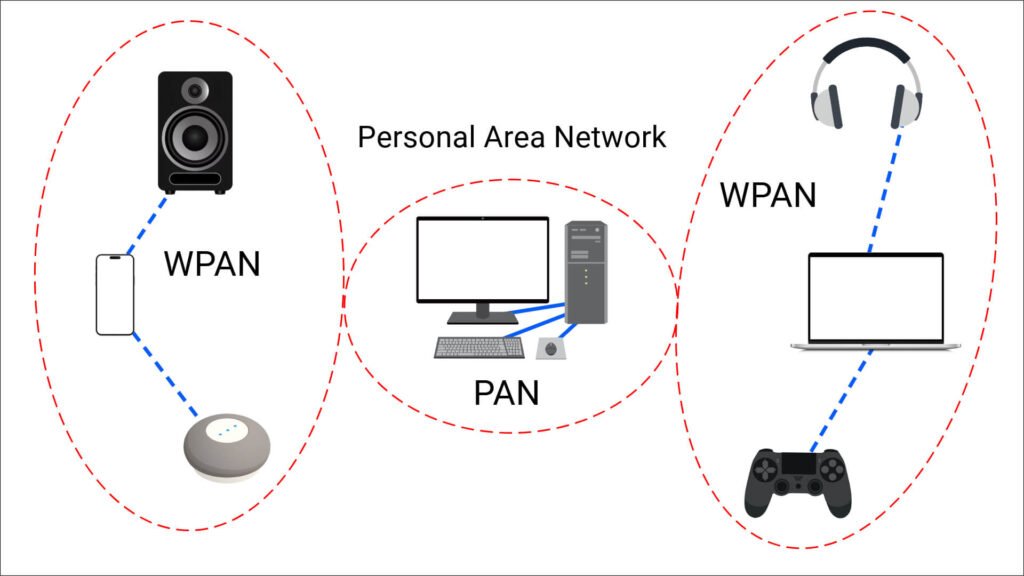
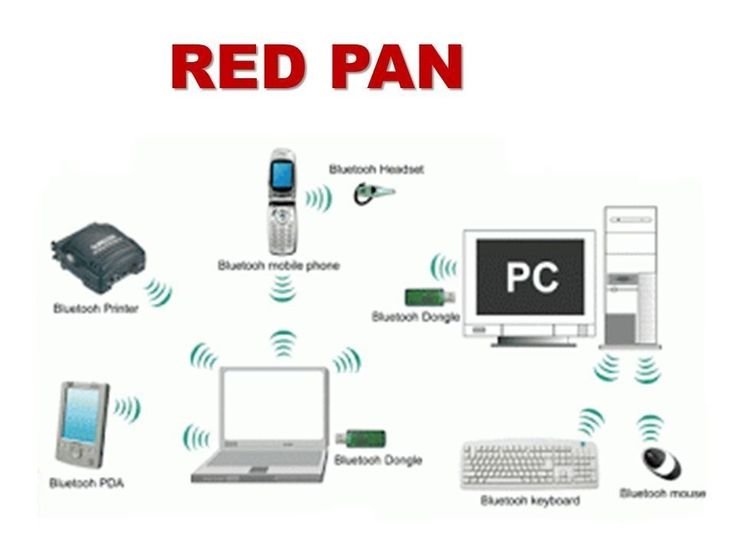
3. Personal Area Network (PAN)
A Personal Area Network (PAN) is designed for personal devices within a very limited range, typically within a few meters. PANs are commonly used to connect devices like smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearable technology.
Characteristics of PAN
- Very Limited Range: PANs usually cover a radius of about 10 meters.
- Low Data Transfer Rates: Speeds are usually lower than LANs, typically up to 1 Mbps.
- Low Cost: Setting up a PAN often involves minimal expense since it typically utilizes Bluetooth or Wi-Fi Direct.
- Simple Management: PANs are easy to set up and manage with minimal configuration.
Common Uses of PAN
PANs are widely used for:
- Connecting personal devices like smartphones to headphones.
- Sharing files between nearby devices.
- Controlling smart home devices from a central hub.
4. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) covers a larger geographical area than a LAN but is smaller than a WAN, typically spanning a city or a large campus. MANs are often used to connect multiple LANs within a specific region, making them ideal for organizations with various locations in a city.
Characteristics of MAN
- City-Wide Coverage: MANs are designed to cover an entire city or a large campus.
- Moderate Data Transfer Rates: Speeds can vary but generally fall between LANs and WANs.
- Cost-Effective: Setting up a MAN can be more economical than WANs, as it often uses existing infrastructure.
- Moderate Complexity: Management is more complex than LANs but less so than WANs.
Common Uses of MAN
MANs are typically utilized for:
- Connecting various branches of a university.
- Linking several offices of a business within a city.
- Providing high-speed internet access to city residents.
Key Differences Between WAN, LAN, PAN, and MAN
Understanding the distinctions between WAN, LAN, PAN, and MAN is essential for choosing the right network type for your needs. Here’s a summary of the key differences:
- Geographical Coverage: LAN (limited), PAN (very limited), MAN (city-wide), WAN (wide area).
- Data Transfer Rates: LAN (high), MAN (moderate), WAN (low to moderate), PAN (low).
- Cost: LAN (low), PAN (low), MAN (moderate), WAN (high).
- Management Complexity: LAN (easy), PAN (easy), MAN (moderate), WAN (complex).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the primary purpose of a LAN?
The primary purpose of a Local Area Network (LAN) is to connect computers and devices within a limited area, allowing for resource sharing, communication, and collaboration among users.
2. How does a WAN differ from a LAN?
A Wide Area Network (WAN) covers a much larger geographical area than a Local Area Network (LAN) and typically has lower data transfer speeds and higher setup costs.
3. What devices are commonly used in a PAN?
Common devices in a Personal Area Network (PAN) include smartphones, tablets, laptops, and wearable technology like smartwatches and fitness trackers.
4. Can a MAN be used for internet access?
Yes, a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) can be used to provide high-speed internet access to users within a city or large campus.
5. Which network type is best for a home setup?
A Local Area Network (LAN) is typically the best choice for home setups, as it provides high-speed connectivity and is easy to manage.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of computer networks—WAN, LAN, PAN, and MAN—is essential for anyone looking to navigate the digital landscape effectively. Each network type serves unique purposes and offers distinct advantages and limitations. By assessing your specific needs and requirements, you can choose the most suitable network type to enhance connectivity, improve communication, and streamline resource sharing. Whether you’re a home user, a small business, or a large corporation, making informed decisions about your network infrastructure will help you reap the benefits of modern technology.
📰 Original Source
Este artigo foi baseado em informações de: https://tecnoblog.net/responde/quais-sao-os-tipos-de-rede-de-computadores-veja-as-diferencas-entre-wan-lan-pan-e-man/